CPR Report Finds India’s Heat Action Plans Lack Targeted Support for Vulnerable Groups
New Delhi, 27th March 2023: Heat Action Plans (HAPs) are India’s primary policy response to economically damaging and life threatening heatwaves. They prescribe a variety of preparatory activities, disaster responses, and postheatwave response measures across state, district, and city government departments to decrease the impact of heatwaves.
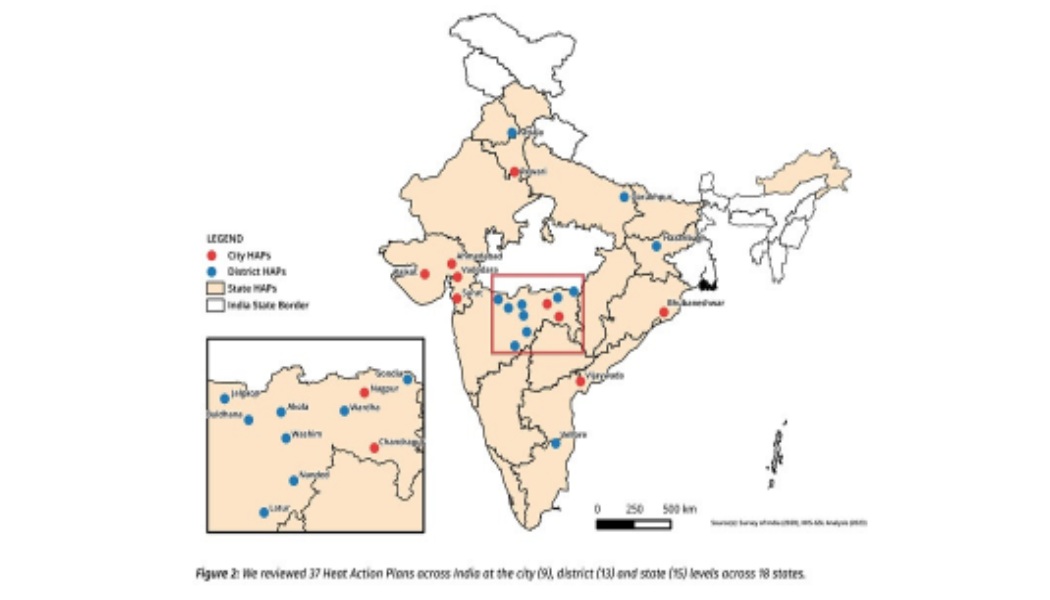
The Centre for Policy Research’s new report, ‘How is India Adapting to Heatwaves?: An assessment of heat action plans with insights for transformative climate action’, assesses 37 HAPs across 18 states to understand how well prepared the country is to deal with heatwaves. This is the first critical assessment of HAPs in India. A list of the states, cities and districts covered in our assessment is here:
Key findings
1. Most HAPs are not built for local contexts: HAPs across the country generally focus on dry extreme heat and ignore the threats posed by humid heat and warm nights. Most HAPs adopt national heatwave thresholds that may not be suited to the risks faced by local populations. Only 10 out of 37 HAPs seem to have locally-specified temperature thresholds. Climate projections, which could help identify future planning needs, are not integrated into current HAPs.
2. Nearly all HAPs fail to identify and target vulnerable groups: Only 2 HAPs carry out and present vulnerability assessments (systematic studies to locate where the people most likely to be affected are in a city, district, or state). While most HAPs list broad categories of vulnerable groups (elderly, outdoor workers, pregnant women), the list of solutions they propose do not necessarily focus on these groups.
3. HAPs are underfunded: Only 3 of 37 HAPs identify funding sources. Eight HAPs ask implementing departments to self-allocate resources, indicating a serious funding constraint.
4. HAPs have weak legal foundations: None of the HAPs reviewed indicate the legal sources of their authority. This reduces bureaucratic incentives to prioritise and comply with HAPs instructions.
5. HAPs are insufficiently transparent: There is no national repository of HAPs and very few HAPs are listed online. It is also unclear whether these HAPs are being updated periodically and whether this is based on evaluation data.
“India has made considerable progress by creating several dozen heat action plans in the last decade. But our assessment reveals several gaps that must be filled in future plans. If we don’t, India will suffer damaging economic losses due to decreasing labour productivity, sudden and frequent disruptions to agriculture (like we saw last year), and unbearably hot cities as heatwaves become more frequent and intense,” said Aditya Valiathan Pillai, Associate Fellow at CPR and co-author of the report.
CPR’s report recommends that HAPs identify sources of financing – either from new funds or by combining actions with existing national and state policies – and set up rigorous independent evaluations as a basis for constant improvement.
“Without implementation-oriented HAPs, India’s poorest will continue to suffer from extreme heat, paying with both their health and incomes”, Pillai added.
Join Punekar News Whatsapp Group, Telegram, Instagram And Twitter For Regular Update about Pune City And Pimpri-Chinchwad








